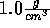 . Insert a noble gas and view its nearest water molecules.
. Insert a noble gas and view its nearest water molecules.
Hydrophobic hydration means the hydration of a non polar or non ionic molecule, such as a noble gas atom. The interaction is represented by the Lennard--Jones potential alone. The water molecules do not specifically reorient towards the inserted molecule; rather they try to build a net around it.
Background :
Hydrophobic hydration describes the hydration of a noble gas atom. In contrast to an ion, the noble gas alone has no charge and therefore cannot have a Coulomb interaction with the water molecules. The attractive and repulsive forces are described solely by the Lennard--Jones potential (section 3.4). In contrast to the hydration of a charged ion, the hydration shell of a noble gas does not destroy the structure of the hydrogen bond network; the water molecules do not orient their charge concentrations towards the inserted particle. As we will see in the following simulation, the noble gas can actually enhance the network structure if the noble gas atom has the right size.
System settings :
Start with the NVT ensemble, fix the temperature at 298 K and the density
at 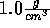 . Insert a noble gas and view its nearest water molecules.
. Insert a noble gas and view its nearest water molecules.
Questions :
Conditions that make the insertion of a non--polar particle into the solvent
more difficult.
Effects of an inserted non--polar particle on the hydrogen bond network.